The immune status of the population has greatly decreased due to anthropogenic pressure, social factors, widespread use of antibiotics, hormonal, chemotherapy, radiation and other factors. Thus, the development of immunological functional ingredients and dietary supplements for nutritional support of the population with weakened immunity is very important.
Muropeptides of postbiotic origin are very promising components, as they have high immunological activity. Muropeptides are the structural components of bacterial peptidoglycans, have all the necessary properties for pathogen-associated molecular structures expressed in the stimulation of innate immunity and the ability to form protection against microbial infectious agents in vertebrates. Exogenous administration of muropeptides reproduces the physiological and evolutionary mechanisms of the immune response.
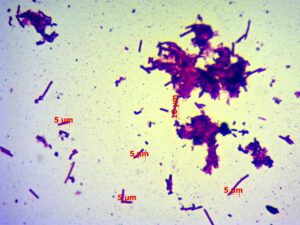
Obtaining and identifying muropeptides is a rather complex and lengthy process. To date, we have developed an easy-to-implement method for the identification of muropeptides and an integrated biotechnological approach to the destruction of probiotic bacteria peptidoglycans. Peptidoglycans destruction was achieved with the following combined methods: biomass autolysis, sonication, enzymatic hydrolysis of the peptidoglycans by proteases and muramidases.
Equipment obtained with the support of U.S.-Ukraine Foundation Biotech Initiative allowed us to optimize and accelerate the research process and the development of modes of technological operations for the production of functional food ingredients and dietary supplements based on muropeptides.
Analytical scales ANZ160C significantly reduce sample preparation time and increase the accuracy of processes, while the digital microscope XS-3330 LED MICROmed allows us to quickly and effectively determine the disintegrating effect of various factors on the integrity of probiotic cells. The use of the digital Portable refractometer RSD501 and Portable pH meter SX-620 allow to optimize the preparation of enzymatic hydrolysis processes, namely, when calculating the concentration of enzymes in the reaction mixture, which depends on the substrate content (concentration of dry substances), and when bringing the pH of the medium to the optimal value for a specific enzyme.
The next stage of our work is obtaining immunological muropeptides by complex processing of the probiotic bacteria cell walls. We also plan to study the physiological activity of the obtained muropeptides, develop technologies for functional food ingredients and dietary supplements based on them, and test the developed products at a biotechnological enterprise.
-Antonina Kapustian, Associate Professor, Head of Department of Food Chemistry and Expertise, Odesa National Academy of Food Technologies
Antonina is the recipient of a small research grant from the US-Ukraine Foundation Biotech Initiative

